Inflation rate from 2012 to 2022
Category : Uncategorized
Inflation rate from 2012 to 2022,(compared to the previous year)
The Survey demonstrates the inflation rate in India from 2012 to 2018, with projections up until 2022. The inflation rate is computed utilizing the cost increment of a characterized item crate. This item bushel contains items and administrations, on which the normal buyer burns through cash consistently. They incorporate costs for foodstuffs, garments, lease, control, media communications, recreational exercises and crude materials (e.g. gas, oil), and also government charges and assessments. In 2018, the inflation rate in India was around 4.74 percent contrasted with the earlier year. See figures on India’s monetary development for extra data.
India’s inflation rate and economy
Inflation is for the most part characterized as the expansion of costs of products and enterprises over a specific time frame, rather than collapse, which portrays a diminishing of these costs. Inflation is a critical financial marker for a nation. The inflation rate is the rate at which the general ascent in the level of costs, products and enterprises in an economy happens and how it influences the average cost for basic items of those living in a specific nation. It impacts the financing costs paid on investment funds and home loan rates yet in addition has a course on levels of state annuities and advantages got. A 4 percent expansion in the rate of inflation in 2011 for instance would mean an individual would need to burn through 4 percent more on the merchandise he was acquiring than he would have done in 2010.
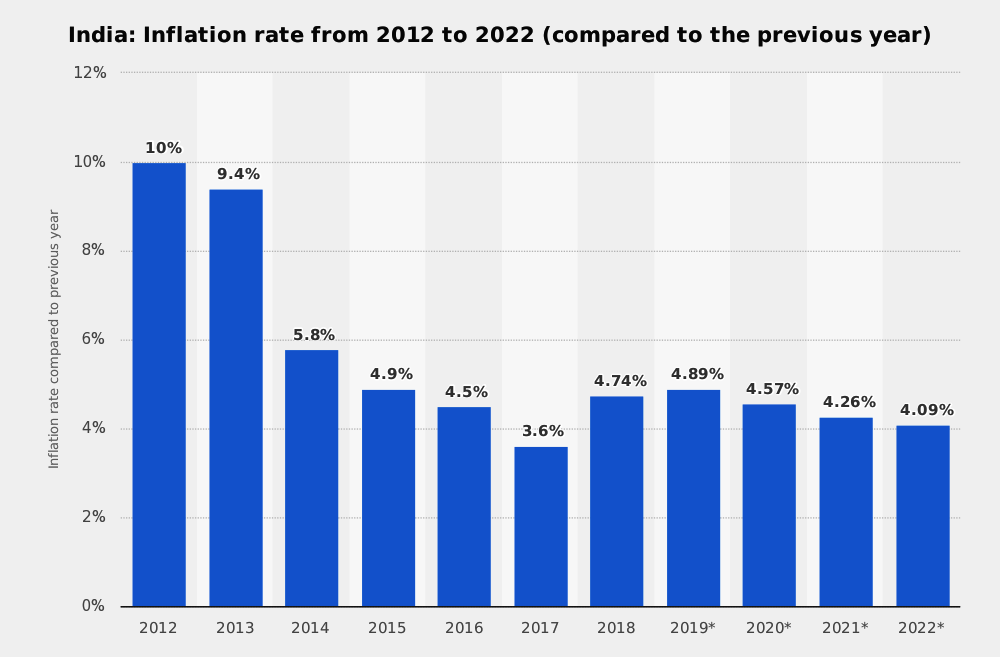
India’s inflation rate has been on the rise over the last decade. However, it has been decreasing slightly since 2010. India’s economy, however, has been doing quite well, with its GDP increasing steadily for years, and its national debt decreasing. The budget balance in relation to GDP is not looking too good, with the state deficit amounting to more than 9 percent of GDP.